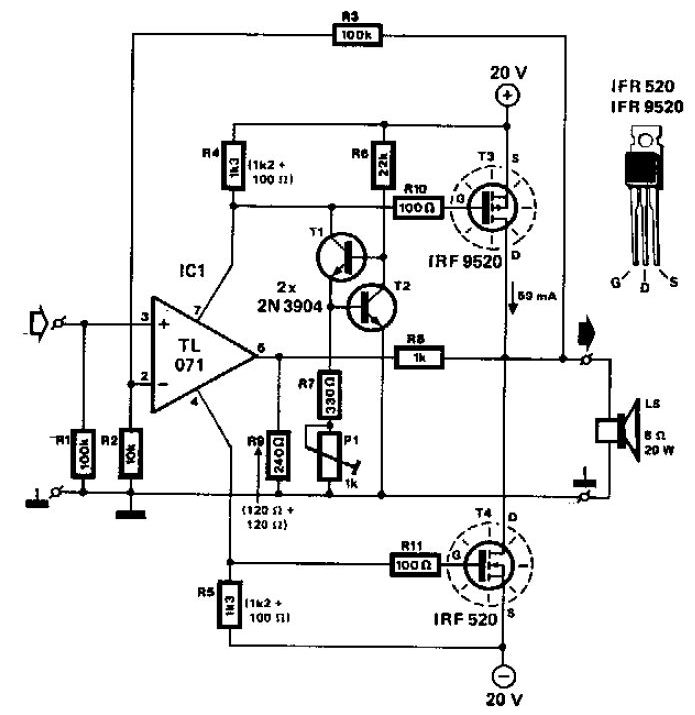
features:
Maximum Output Power : 68W RMS - 108W Peak
THD : %0.03 at 60W
SNR : 110dB at 60 W - 92.5dB at 1W
PSRR : 120dB
Protection Circuitries : DC /AC Short circuit protection and thermal protection
Output Class : Conjugate AB-A
[source]
Home » Posts filed under Audio Circuit
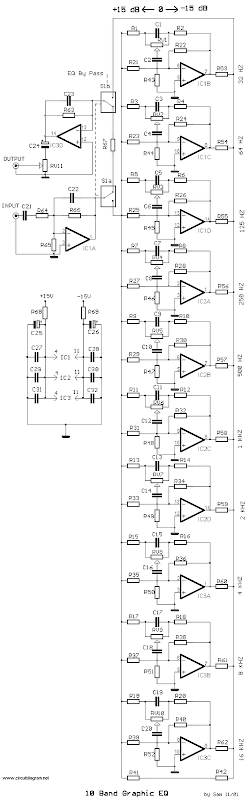
Graphic Equalizer Schematic 10 band Mono Part List: |
| R1....20= 10Kohms | C4= 10nF polyester | C18= 68pF polysterine |
| R21....40= 1Mohms | C5= 47nF polyester | C19= 360pF polysterine |
| R41= 10Kohms | C6= 4.7nF polyester | C20= 36pF polysterine |
| R42= 1Kohms | C7= 22nF polyester | C21= 4.7uF polyester |
| R43.....52= 2.2Kohms | C8= 2.2nF polyester | C22-23= 33pF polysterine |
| R53.....62= 47Kohms | C9= 12nF polyester | C24= 10uF 25V |
| R63-64-66-67= 47Kohms | C10= 1.2nF polyester | C25-26= 47uF 25V |
| R65= 10Kohms | C11= 5.6nF polyester | C27...32= 47nF polyester |
| R68-69= 47 ohms 1/2W | C12= 560pF polysterine | IC1...3= TL074 |
| RV1....10= 100Kohms lin FADER | C13= 2.7nF polyester | S1= 2X4 SW for stereo |
| RV11= 10Kohms log. | C14= 270pF polysterine | |
| C1= 180nF polyester | C15= 1.5nF polyester | |
| C2= 18nF polyester | C16= 150pF polysterine | |
| C3= 100nF polyester | C17= 680pF polysterine |
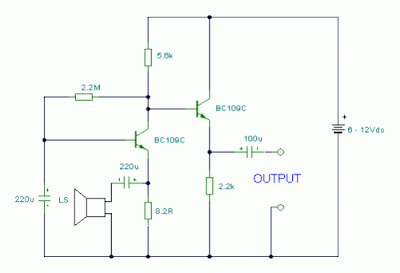
This circuit corrects the problem somewhat and allows a larger voltage swing and probably more output power, but I don't know how much without doing a lot of testing. The output still won't move more than a couple volts using small transistors since the peak current won't be more than 100mA or so into a 25 ohm load. But it's an improvement over the other circuit above.
In this circuit, the 1K load resistor is tied to the speaker so that as the output moves negative, the voltage on the 1K resistor is reduced, which aids in turning off the top NPN transistor. When the output moves positive, the charge on the 470uF capacitor aids in turning on the top NPN transistor.
The original circuit in the radio used a 300 ohm resistor where the 2 diodes are shown but I changed the resistor to 2 diodes so the amp would operate on lower voltages with less distortion. The transistors shown 2n3053 and 2n2905 are just parts I used for the other circuit above and could be smaller types. Most any small transistors can be used, but they should be capable of 100mA or more current. A 2N3904 or 2N3906 are probably a little small, but would work at low volume.
The 2 diodes generate a fairly constant bias voltage as the battery drains and reduces crossover distortion. But you should take care to insure the idle current is around 10 to 20 milliamps with no signal and the output transistors do not get hot under load.
The circuit should work with a regular 8 ohm speaker, but the output power may be somewhat less. To optimize the operation, select a resistor where the 100K is shown to set the output voltage at 1/2 the supply voltage (4.5 volts). This resistor might be anything from 50K to 700K depending on the gain of the transistor used where the 3904 is shown.